Instructions for Assembling Vortex Relay Controller¶
Brief Description¶
- We need to a way to keep our Beads evenly suspended before an injection.
- We can use Vortices to keep our beads suspeneded.
- However, we don't want to keep these Vortices turned on all the time.
- Keeping them on all the time can shear the beads into smaller fragments.
- It becomes difficult to Load the Beads or change the 50ml Tubes if the vortex is Turned on all the time.
| Location of Vortex Stirrer(s) in Schematic |
|---|
 |
Ordering the Parts¶
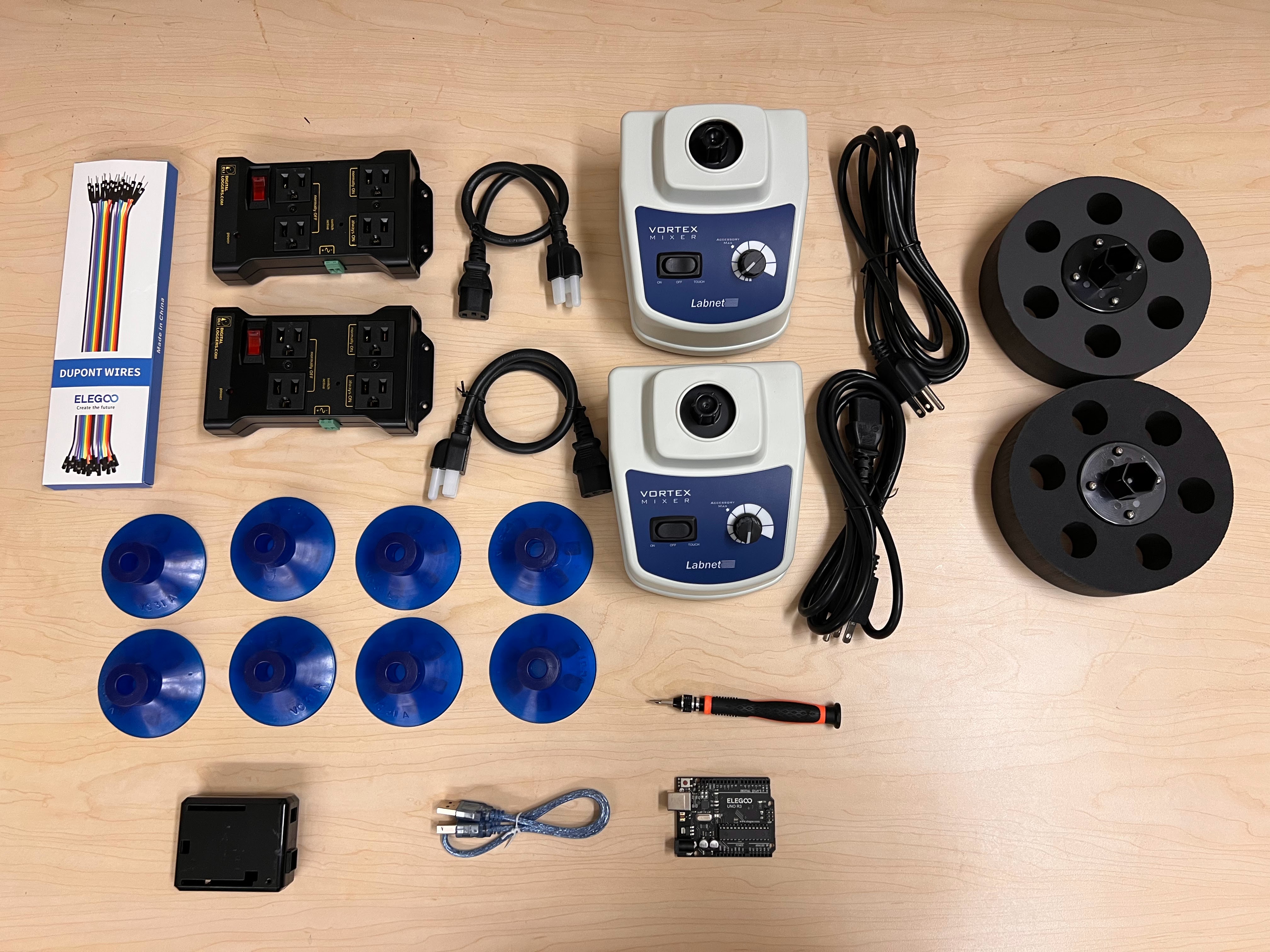
- You will need the following parts:
- We used the 3mm Flat Head for our screwdriver for the next part.
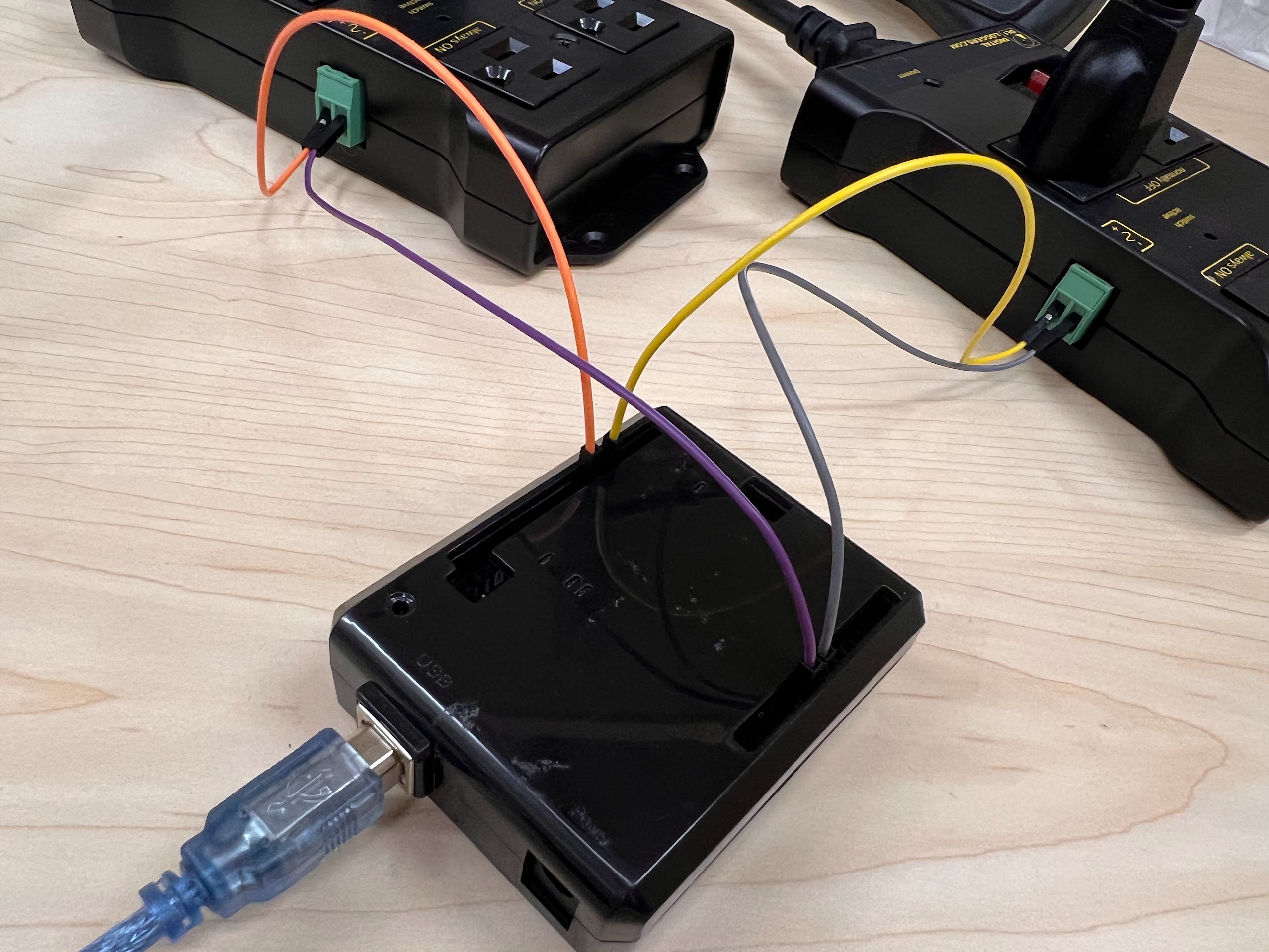
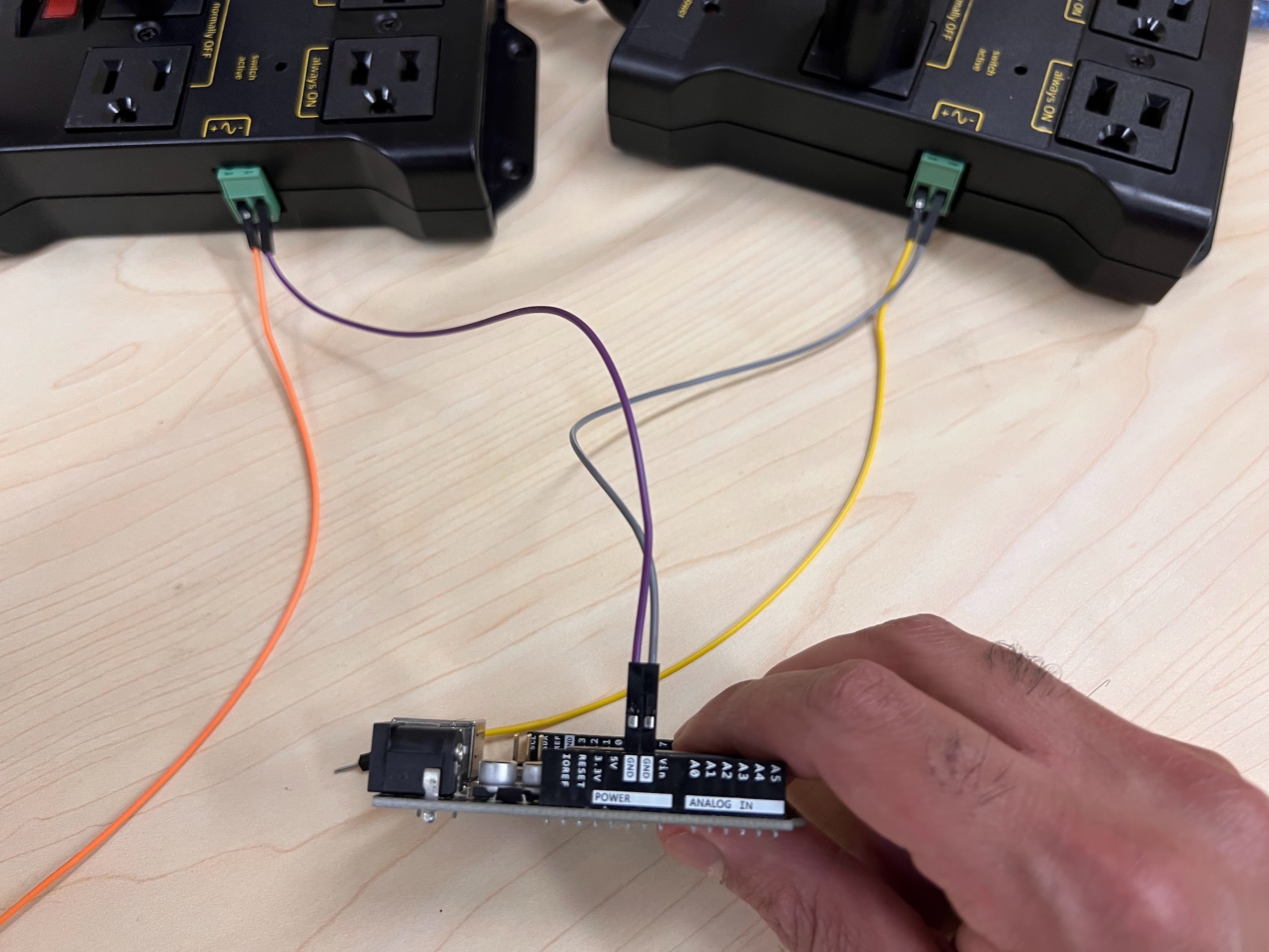
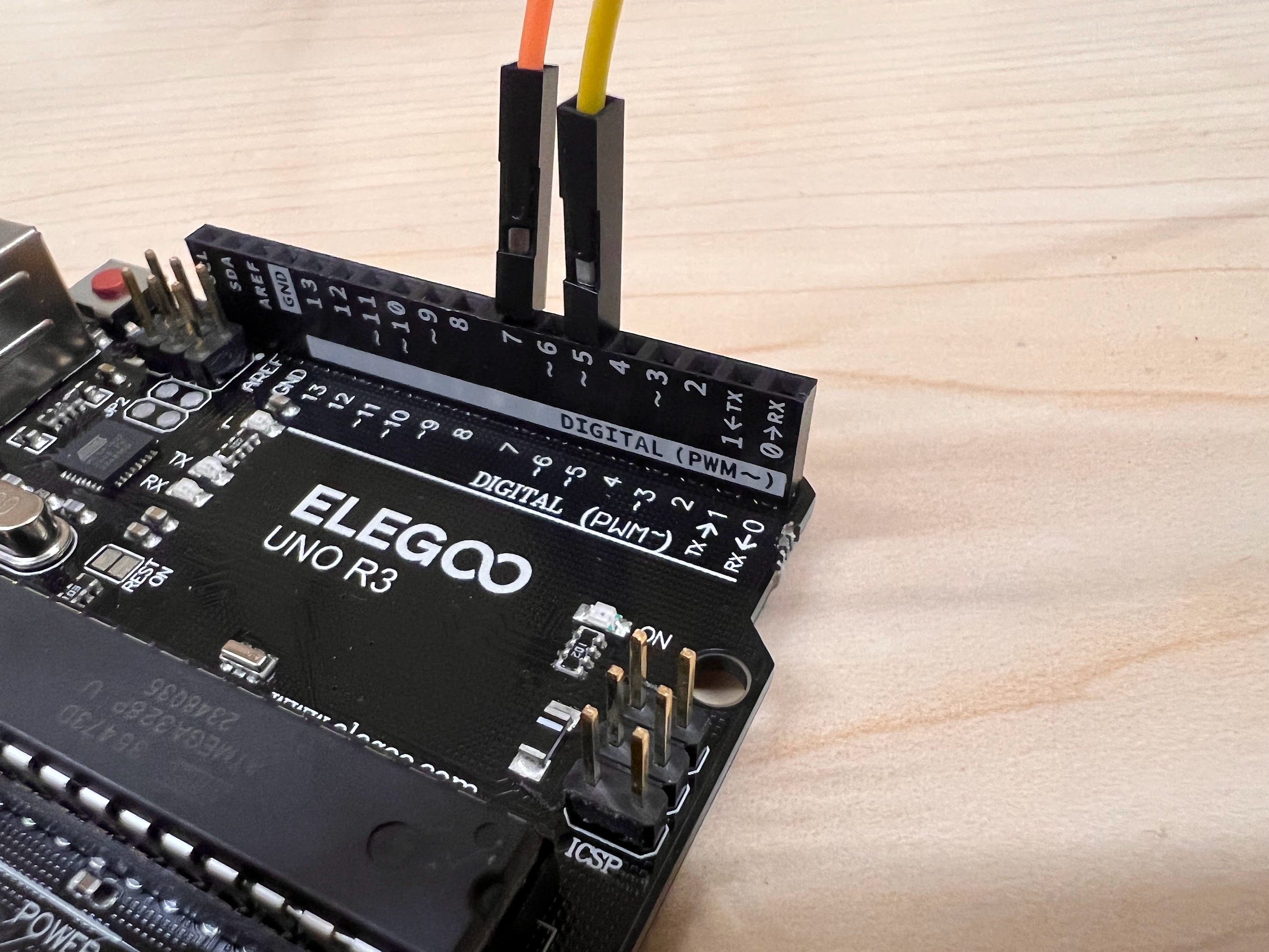
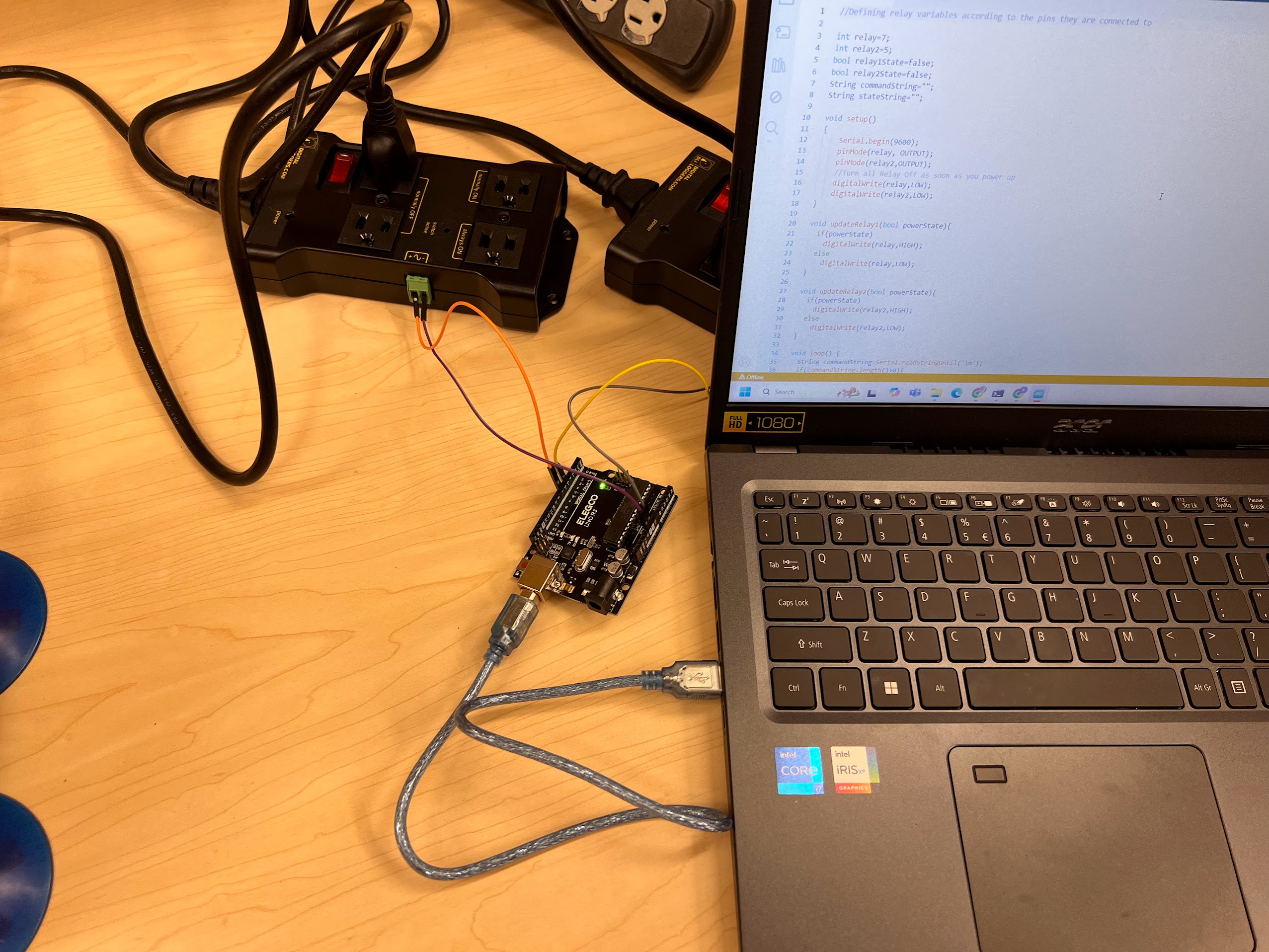
- Execute the cell below to learn how to wire up your Vortices to the AC Relay Boxes.